Configuring with a Telnet Console¶
An alternative configuration method is the Telnet method, and it is described in this chapter.
Telnet¶
Telnet is a remote terminal software to login to any remote telnet servers. It is typically installed in most of the operating systems. To use it, users open a command line terminal (e.g., cmd.exe for Windows Operating System). Note that only users with administrator (admin) access right as configured in Section 2.3 can use telnet to login to the device.
Telnet Log-in¶
After the command line terminal is opened, type in “telnet 192.168.2.1/24” as shown in Figure 4.1. Note that telnet command needs to follow by IP address or domain name. In this example, the default IP address is 192.168.2.1/24 If users change the switch IP address, the IP address to log-in should be changed to match the new switch IP address.
Command Line Interface for Telnet¶
After input the telnet command line, the switch’s interface is displayed as shown in Figure 4.2.
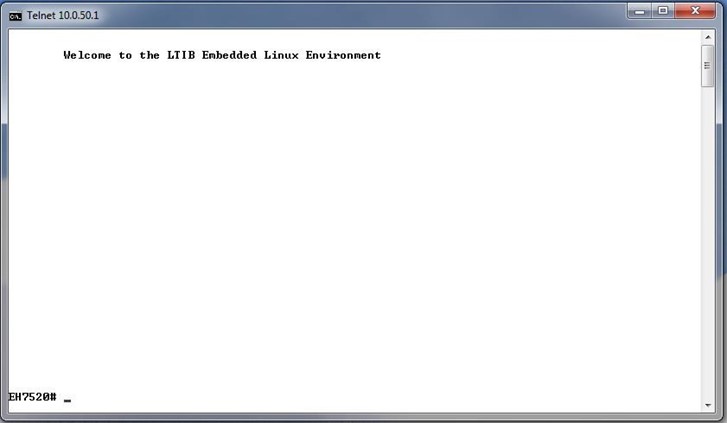
Users will see the welcome screen to the switch interface. From Chapter 3, configuring through telnet is like configuring through the serial console. Users are automatically logged into the privileged mode. The configuration commands are also like the serial console methods. (Please refer to Chapter 2 for more information on configuration).
Commands in the Privileged Mode¶
When users do not know the commands to use for the command line configuration, users type in “?” and the commands are displayed on screen as shown in Figure 4.3.
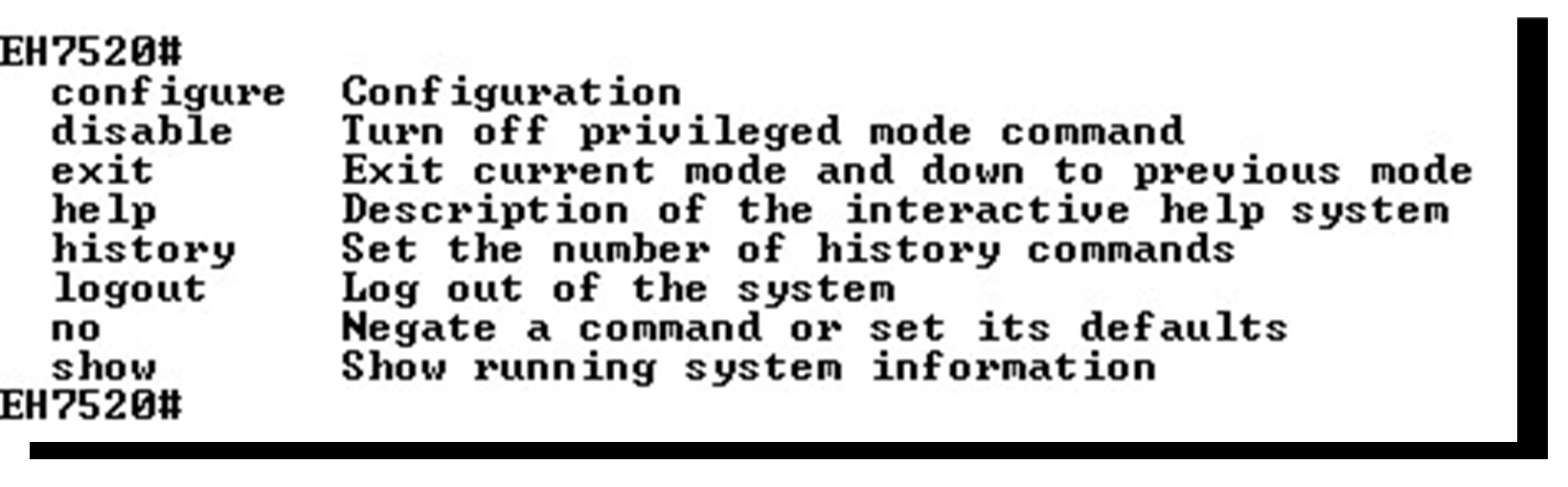
Commands in the Configuration Mode¶
When users type in “?” in configuration mode, a long list of commands isdisplayed on screen as shown in Figure 4.4. Table 4.1 shows all commands that can be used to configure the switch in the configuration mode.
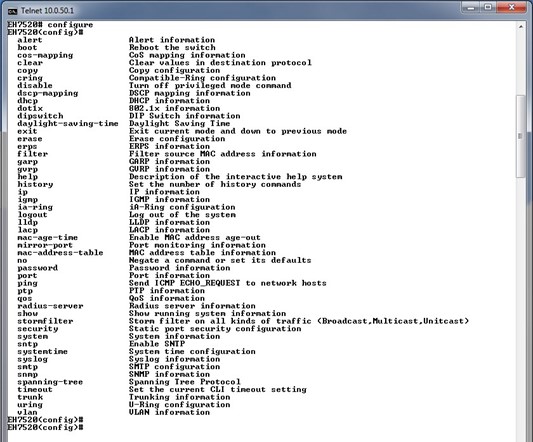
Table 4.1 Commands in the Configuration Mode:
Commands |
Descriptions |
|---|---|
alert |
Alert information |
boot |
Reboot the switch |
cos-mapping |
CoS mapping information |
clear |
Clear values in the destination protocol |
copy |
Copy configuration |
cring |
Compatible-Ring configuration |
disable |
Turn off the privileged mode command |
dscp-mapping |
DSCP mapping information |
dhcp |
DHCP information |
dot1x |
802.1x information |
daylight-saving-time |
Daylight Saving Time |
exit |
Exit the current mode and moveto the previous mode |
erase |
Erase the configuration |
erps |
ERPS information |
filter |
Filter the information of the source MAC address |
garp |
GARP information |
gvrp |
GVRP information |
help |
Description of the interactive help system |
history |
Set the number of history commands |
ip |
IP information |
igmp |
IGMP information |
ia-ring |
iA-Ring configuration |
logout |
Log out of the system |
lldp |
LLDP information |
lacp |
LACP information |
mac-age-time |
Enable age-out time for the MAC address |
mirror-port |
The monitoring information of a Port |
mac-address-table |
Information of the MAC address table |
no |
Negate a command or set to its defaults |
password |
Password information |
port |
Port information |
ping |
Send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to network hosts |
ptp |
PTP information |
qos |
QoS information |
radius-server |
Radius server information |
show |
Show information of the current running system |
stormfilter |
Storm filter on all kinds of traffic (Broadcast,Multicast,Unitcast) |
security |
Security configuration of a static port |
system |
System information |
sntp |
Enable SNTP |
systemtime |
Configuration of the system time |
syslog |
Syslog information |
smtp |
SMTP configuration |
snmp |
SNMP information |
spanning-tree |
Spanning Tree Protocol |
timeout |
Set the current CLI timeout |
trunk |
Trunking information |
uring |
U-Ring configuration |
vlan |
VLAN information |
Note: Please see Chapter 3 for the details of switch configuration.